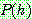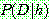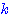 Gaussians
GaussiansBAYESIAN LEARNING
Machine learning : Tom Mitchell 저, McGRAW-HILL, 1997, Page 154~199
3. BAYES THEOREM AND CONCEPT LEARNING
(1) Brute-Force Bayes Concept Learning
(2) MAP Hypotheses and Consistent Learners
4. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND LEAST-SQUARED ERROR HYPOTHESES
5. MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD HYPOTHESES FOR PREDICTING PROBABILITIES
(1) Gradient Search to Maximize Likelihood in a Neural Net
6. MINIMUM DESCRIPTION LENGTH PRINCIPLE
(1.1) ESTIMATING PROBABILITIES
10. AN EXAMPLE : LEARNING TO CLASSIFY TEXT
(4) Learning Bayesian Belief Networks
(5) Gradient Ascent Training of Bayesian Networks
(6) Learning the Structure of Bayesian Networks
(1) Estimating Means of 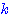 Gaussians
Gaussians
(2) General Statement of EM Algorithm
(3) Derivation of the 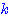 Means Algorithm
Means Algorithm
13. SUMMARY AND FURTHER READING
p154
p155
p156
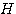


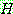
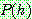
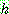
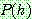
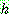
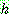
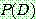



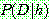

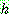
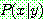
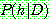

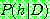
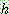
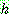

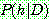

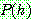

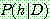
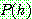
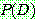
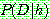
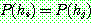
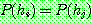
Bayes theorem :
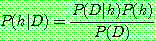 (1)
(1)
p157
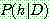
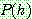
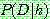
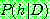
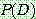

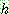

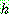
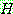
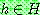


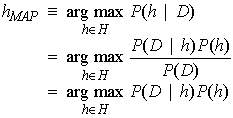 (2)
(2)
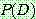
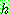
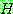
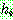
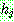
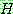
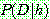
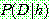

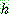
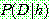
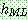
![]() (3)
(3)



p158
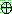
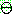
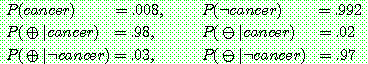


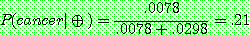
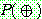
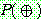


p159
표 1
|
|
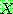
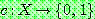

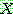
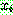 (i.e.,
(i.e.,  )
) 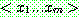

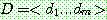
BRUTE-FORCE MAP LEARNING algorithm
1. 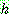
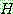
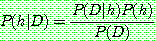
2. ![]()
p160
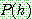
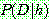
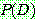
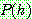
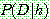
1. 

2. 
3.
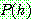
 for all
for all  in
in 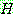
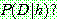
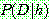
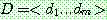
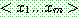
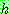
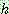
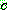
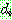
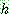
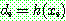
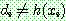
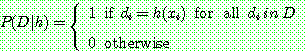


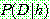
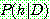
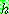

p161
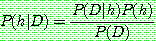
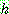

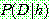

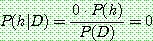 if
if 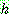 is inconsistent with
is inconsistent with 

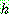

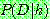
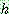

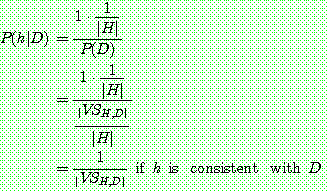
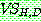
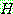

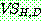
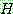

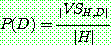
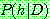
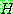

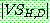
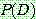
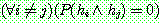
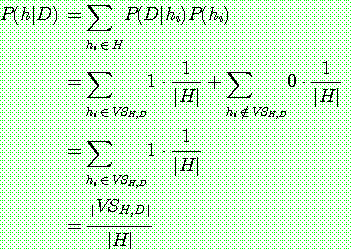
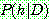
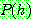
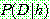
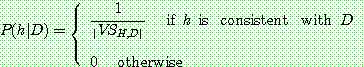 (5)
(5)
p162
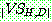
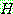

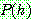
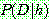
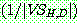

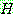
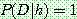

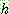
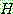
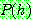
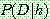
data.gif)
그림 1
p163
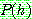
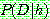
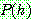
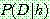
![]()
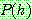
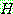
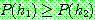
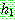
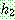
![]()
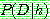
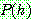
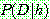
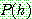
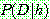
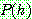
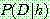
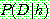
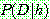
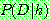
p164
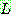
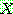
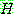
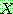
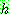
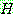
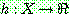
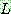
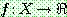
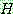
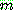
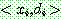
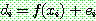
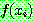
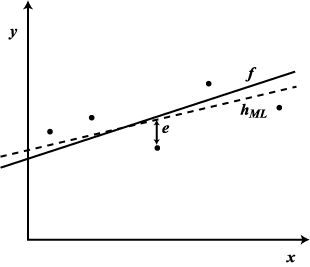
그림 2
p165
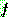
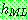
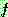
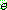
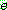
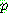
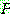
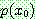
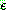
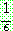
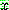
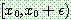
Probability density function:
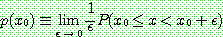
![]()
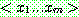

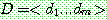
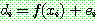
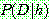
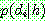
![]()
p166
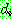
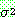
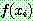
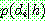
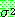
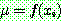
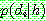
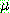
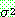
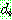
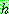
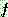
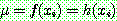
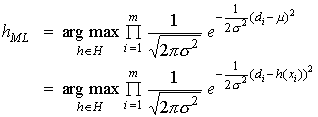
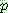
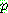
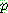
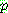
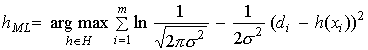
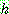
![]()
![]()
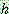
![]() (6)
(6)
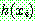
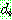
p167
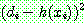
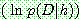
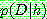
p168
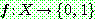
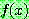
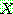
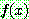
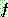
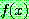
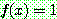

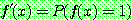
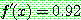
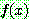
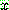
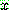
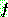
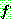
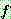
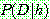


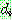
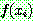
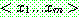
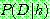
![]() (7)
(7)
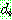
p169
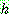
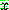
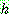
![]() (8)
(8)


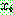
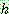
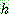
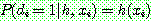
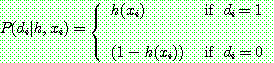 (9)
(9)
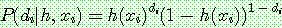 (10)
(10)

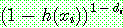
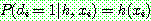


![]() (11)
(11)
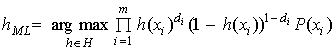
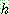
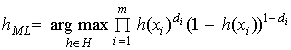 (12)
(12)
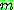

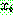
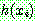
p170
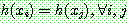
![]() (13)
(13)
![]()
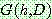
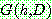
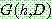
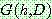
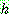
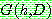
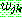
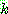

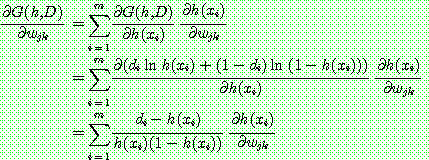 (14)
(14)
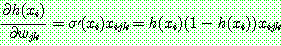
 th
th 
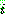 th
th 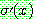
p171
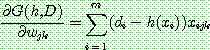
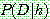
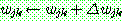
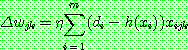 (15)
(15)
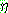
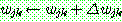
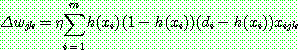 (16)
(16)
p172


![]()
![]()
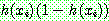
![]() (16)
(16)
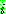

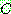

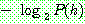
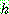
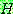
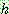

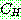
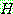
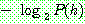

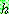
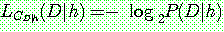


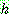
p173

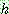
![]()
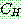

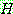

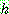
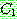
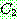

![]() (17)
(17)

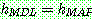
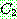
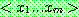
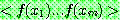

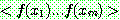
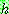
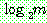
p174

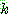
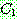


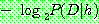
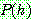
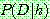
p175
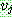
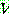
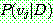
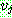

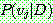
![]() (18)
(18)

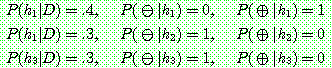
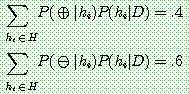

p176
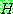
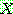
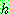
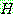
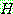
1. 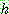
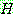
2. 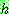
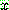
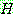
p177
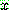
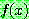
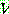
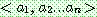
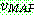
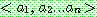
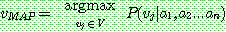
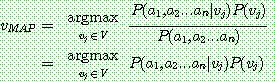 (19)
(19)
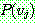
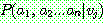
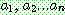
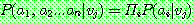
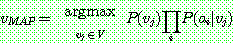 (20)
(20)
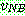
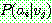
p178
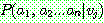
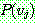
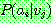
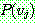
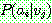
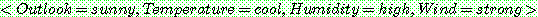
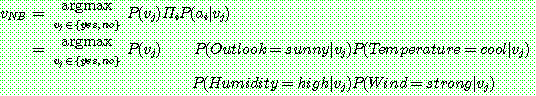 (21)
(21)
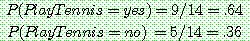
p.179

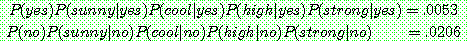
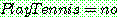
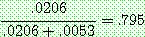
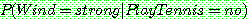
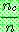
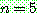
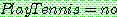


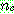
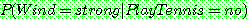
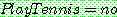
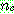
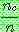

 (22)
(22)
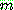
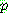
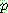
p180
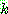

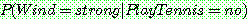
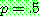
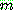
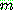 -estimate
-estimate 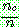
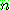
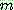
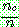
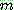
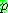
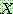
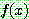
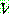
p181
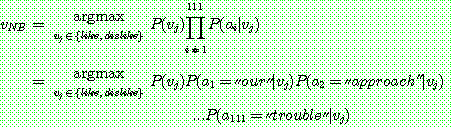
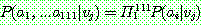
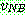
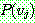
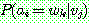
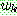
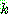 th
th 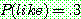
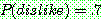

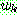
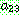
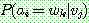
p182

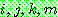


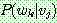
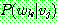
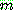
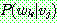
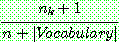
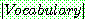
p183
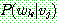
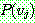
1.
2. 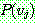
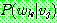


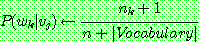
![]()
p184
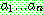
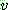
p185

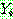
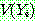
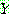
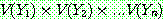


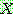
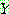
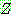
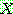
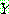
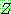
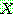
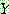
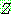
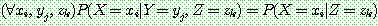
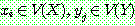

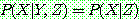

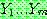

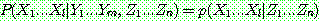
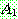
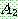
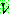
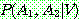
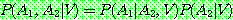 (23)
(23)
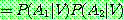 (24)
(24)
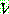
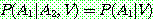
p186
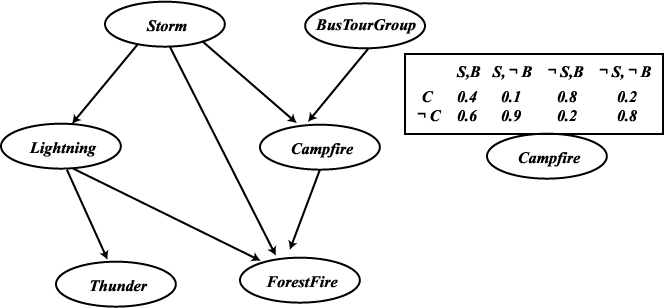
그림 3
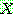


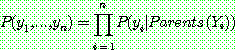

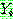

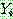
p187

p188
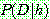
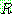
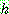
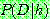
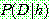
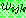
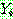
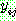
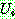
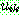
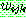
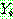
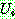
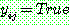
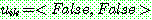
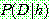
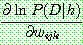
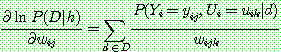 (25)
(25)
p189
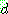

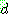
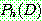
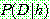
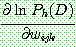


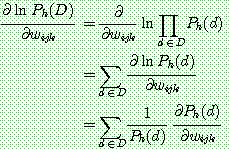
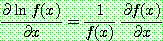


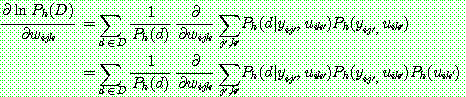

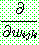

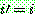
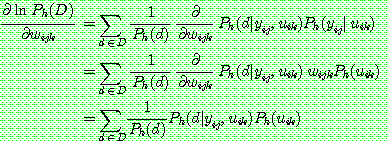
p190
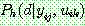
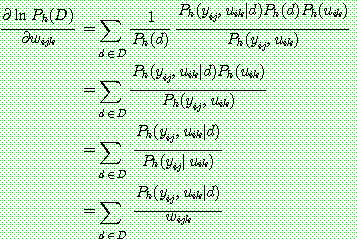 (26)
(26)
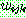
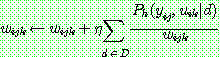
p191
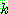 Gaussians
Gaussians
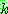
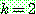

p192
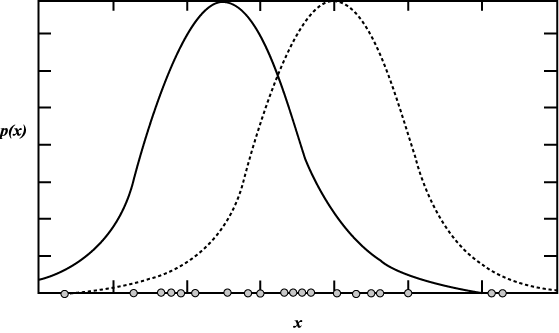
그림 4
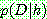
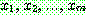
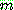
![]() (27)
(27)
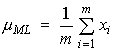 (28)
(28)
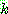
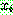
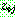
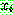
 th
th 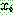

p193
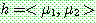
Step 1 : 
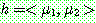
Step 2 : 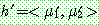
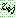

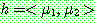
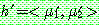

 th
th
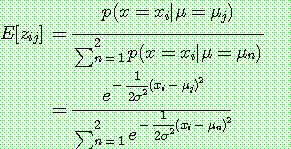
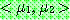
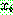

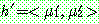
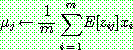
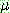

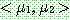
p194
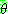
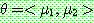
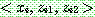
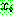
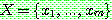
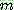
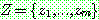
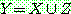
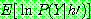
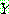
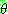
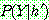
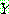
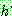
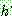
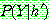
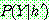
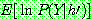
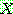
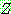
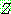
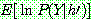
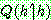
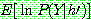
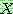
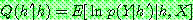
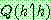
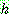
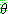
p195
Step 1 : 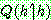
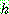
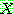
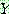
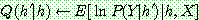
Step 2 : 
![]()
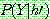
 Means Algorithm
Means Algorithm
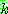


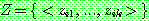
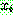
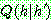
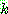
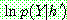
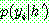
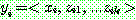
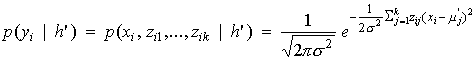
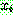
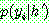
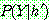
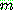
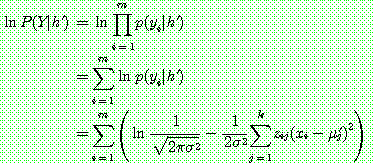
p196
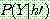
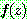

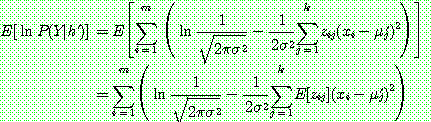
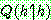
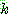
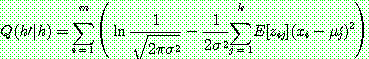
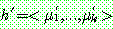

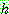
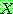
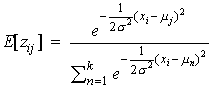 (29)
(29)

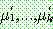
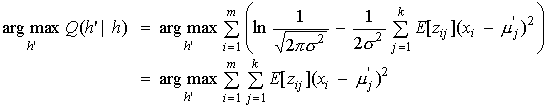 (30)
(30)
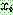
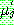

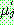
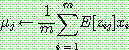 (31)
(31)
p197
p198
1. ¬cancer
2. 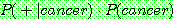
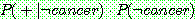

3. (a) 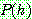
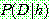
(b) 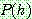
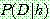
(c) 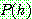
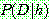
5. 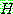
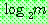
(c)